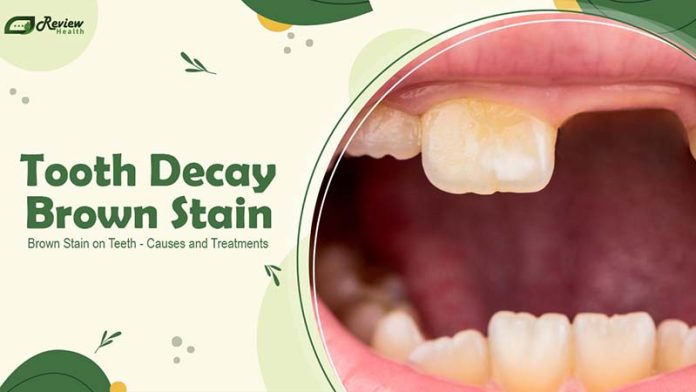
Welcome to Review Health, where we delve into everything you need to know about tooth decay brown stain on teeth. We’ll explore the causes of these marks, preventive measures, and the most effective treatments available. A vibrant and healthy smile is crucial not just for aesthetic reasons but for overall oral health as well. This guide offers detailed insights into the reasons behind tooth discoloration and provides professional advice to help you maintain excellent dental hygiene. Learn how to effectively prevent and treat these prominent brown spots for a healthier, brighter smile.
Top 12 Major Causes of Tooth Decay Brown Stain
Discovering brown stains on your teeth can be unsettling. These blemishes are not only a cosmetic concern but often indicate underlying health issues. The causes of tooth decay brown stain on teeth are varied, ranging from lifestyle choices to medical conditions. In this section, we will explore twelve common factors that can lead to brown spots on your teeth. Understanding these can help you take preventive measures or seek appropriate treatments to maintain your dental health and restore the natural beauty of your smile.

1. Nicotine
Nicotine from cigarettes and other tobacco products is a major culprit behind tooth decay brown stain on teeth. Smoking not only affects your lungs but also leaves persistent stains on your teeth due to the tar and nicotine content.
2. Foods and Beverages
Regular consumption of certain foods and beverages, including coffee, tea, sodas, and dark berries, can lead to brown tooth decay. These items have potent colorants that adhere to the enamel and stain the teeth over time.
3. Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is a significant factor in the development of brown spots. As decay progresses, it can cause discoloration, which often manifests as brown stains on the affected teeth.
4. Tartar
When plaque on teeth hardens, it turns into tartar, which is much more difficult to remove. Tartar buildup can lead to brown spots near the gum line, contributing to overall tooth discoloration.
5. Fluorosis
Excessive fluoride intake during the early years of tooth development can lead to fluorosis, characterized by white streaks or brown spots on the teeth, which are indications of enamel damage.
Dig deeper: Does Fluoride Cause Tooth Decay? Understanding the Role of Fluoride in Preventing Cavities
6. Enamel Hypoplasia
Enamel hypoplasia occurs when tooth enamel does not form correctly, which can result in thin or weak enamel. This condition makes teeth more prone to staining and decay, often showing as brown spots.
7. Root Canal
Following a root canal treatment, teeth can sometimes darken, taking on a grayish-brown tint due to changes in the tooth’s mineral structure or residual decay.
8. Trauma
Physical injury to teeth can disrupt enamel formation in young children or cause discoloration in adults due to bleeding within the tooth, presenting as brown or gray spots.
9. Old Dental Work
Materials used in older dental restorations, such as silver amalgam fillings, can cast a grayish-brown shadow on the tooth structure, making the teeth appear stained.
10. Medications
Certain medications, particularly tetracycline antibiotics taken during tooth formation, are known to cause brown or gray discoloration as a side effect.
11. Chlorhexidine Mouthwash
Using chlorhexidine-based mouthwashes for extended periods can lead to brown stains on teeth. These mouthwashes are typically prescribed for treating gum disease.
12. Celiac Disease
Celiac disease can affect tooth enamel integrity and lead to the development of yellow-brown spots, indicative of damage and decay.
How to Treat Brown Spots on Teeth
Brown spots on teeth, indicative of tooth decay brown stain on teeth, can detract from your smile and suggest deeper oral health issues. Here’s how you can address these discolorations through comprehensive treatment methods:

- Enamel Hypoplasia: This condition requires diligent oral hygiene to prevent further progression of brown tooth decay. Treatments such as dental sealants or bonding can effectively protect vulnerable enamel from further erosion. Sealants provide a protective layer over the enamel, preventing decay from penetrating the teeth, while bonding involves applying a tooth-colored resin that hardens and meshes with the surface of the teeth, shielding them from external damage and decay.
- At-Home Whitening Treatments: These are suitable for lifting surface stains that lead to brown spots. It’s critical to consult with a dental professional before beginning any whitening regimen to ensure compatibility with your dental health. Options include:
- Whitening kinds of toothpaste: Mild abrasives and polishing agents remove stains on the surface but are less effective on deep discoloration.
- Bleaching Kits: These typically feature peroxide-based gels applied via trays, strips, or a brush. They can alter the intrinsic color of the tooth if used as directed.
- Whitening Strips: Coated with a peroxide-based whitening gel, these strips conform to the shape of your teeth, applying bleaching agents directly to the enamel. Regular application as per product guidelines is necessary to maintain whitening effects. Overuse can lead to enamel degradation, so moderation is key. Look for products with the ADA Seal of Acceptance, which guarantees safety and effectiveness in removing brown tooth decay stains.
Professional Whitening Procedures: When home remedies are insufficient for severe brown spots, professional treatments can be more effective:
- Dental Prophylaxis: Beyond simple cleaning, this preventative treatment helps to stave off cavities and gum disease, both contributors to tooth discoloration.
- Chairside Whitening: This method involves applying a high-concentration peroxide gel to the teeth and is often activated by a special light or laser, enhancing its effectiveness and reducing treatment time.
- Power Bleaching: A more intensive option for stubborn stains, using stronger bleaching agents that penetrate deeper into the enamel.
- Porcelain Veneers: These are ideal for irreversible stains or damaged enamel. Veneers are thin layers of ceramic that are bonded to the front of the teeth, completely covering any discolorations.
- Composite Bonding: This method not only masks stains but also reshapes teeth that are chipped, gapped, or unevenly worn. The composite material is sculpted directly onto the teeth and cured with high-intensity light.
How to Prevent Brown Spots on Teeth
Preventing tooth decay brown stain on teeth not only enhances your smile but also contributes significantly to your overall dental health. Implementing effective oral hygiene practices and making wise lifestyle choices are key steps in maintaining a bright, white, and spot-free smile. Here are some detailed strategies:

Brush and Floss Regularly: Regular dental care is the cornerstone of good oral health. Brush your teeth thoroughly after every meal and floss at least once a day to eliminate food particles and plaque that accumulate on and between teeth. Plaque can harden into tartar, a major contributor to tooth decay and discoloration.
Quit Smoking: Tobacco products, including cigarettes, cigars, and chewing tobacco, are among the leading causes of tooth staining. Smoking also impairs the mouth’s ability to fight off infection, leading to more severe oral health problems. Quitting smoking will significantly reduce the risk of brown spots and improve your overall oral and systemic health.
Watch Your Diet: What you eat and drink can have a significant impact on the color of your teeth. Beverages like coffee, tea, and red wine are known to stain teeth. Always brush or rinse your mouth after consuming these to minimize their staining effect. Additionally, include calcium-rich foods in your diet such as milk, cheese, and leafy greens to strengthen enamel and protect against erosion.
Limit Sugary Foods and Drinks: Sugar is a major enemy of dental health, contributing to the formation of cavities and enamel wear. Frequent consumption of sugary foods and drinks, such as sodas, candies, and desserts, can lead to tooth decay and the subsequent development of brown stains. Choose healthier snack alternatives like nuts, fruits, and vegetables, and reduce your consumption of simple carbohydrates, which can convert to sugars in the mouth and promote plaque formation.
By adopting these comprehensive oral hygiene practices and making informed dietary choices, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing brown tooth decay and maintain a healthier, more attractive smile.
How to Recognize Tooth Decay or Brown Spots on Teeth ?
Understanding how to spot tooth decay brown stain on teeth is key to maintaining your dental health. Tooth decay, commonly referred to as cavities, arises when acids produced by plaque and bacteria erode the tooth enamel. This erosion often presents as yellowish-brown or dark spots.
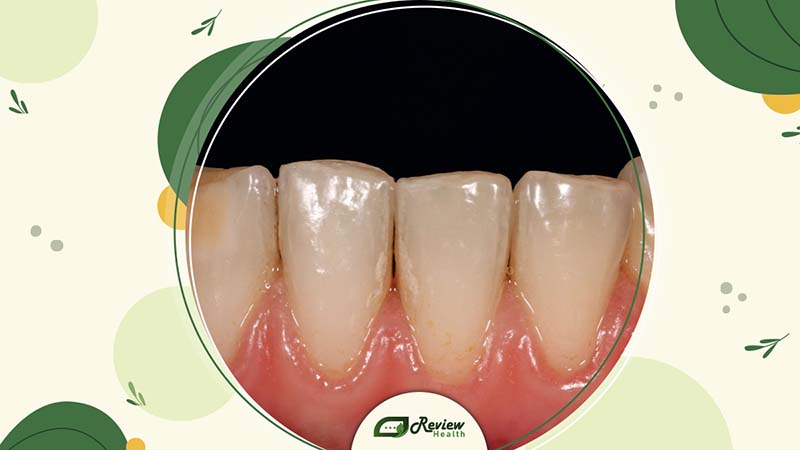
Sources of Brown Spots
Brown spots on teeth can result from a variety of factors:
-
Poor Oral Hygiene: Neglecting regular brushing and flossing allows plaque to accumulate, leading to discoloration.
-
Smoking: Tobacco products can leave stubborn stains on teeth.
-
Diet: Consuming foods and drinks with dark pigments, such as coffee, tea, and red wine, can stain teeth over time.
-
Excessive Fluoride: High levels of fluoride during tooth development can cause fluorosis, which appears as white or brown spots on the teeth.
-
Medical Conditions: Certain health issues, like celiac disease, can affect tooth enamel and lead to discoloration.
Identifying Signs of Tooth Decay and Brown Spots:
Discoloration: Watch for brown, yellow, or white spots on your teeth. If these spots don’t go away with regular brushing and dental cleaning, they could be signs of deeper issues.
Texture Changes: Check the surface of your teeth for any roughness or irregular texture. These changes can signal enamel damage, which often precedes decay and staining.
Enamel Weakness: Be alert to signs of enamel weakening, such as increased sensitivity or transparency in your teeth. Weak enamel is more prone to decay and can lead to discoloration.
Additional Symptoms:
Brown spots on teeth may be accompanied by other oral health symptoms, particularly when related to underlying conditions:
-
Dry Mouth: A lack of saliva, which helps clean teeth naturally, can exacerbate tooth decay and discoloration.
-
Canker Sores and Mouth Ulcers: These issues might appear with discoloration in conditions like celiac disease.
-
Professional Consultation: If you notice these symptoms alongside changes in tooth color, it’s important to consult with a dental professional. They can provide a comprehensive evaluation and recommend the best treatment options.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a brown tooth always a sign of a cavity?
Not necessarily. Although tooth decay can cause brown discoloration as it damages the enamel and deeper layers, not all brown spots are cavities. They can also be stains from foods, drinks, or smoking. It’s important to see a dentist for a proper diagnosis to determine the cause.
Can a brown tooth be restored?
Yes, it’s often possible to save a brown tooth. If the discoloration is due to decay, treatments like fillings, crowns, or even a root canal might be required. For stains from external sources, such as coffee or tobacco, professional dental cleanings or whitening treatments can effectively restore the tooth’s natural color.
Do genetics influence brown stains on teeth?
Yes, genetics can play a role. Some people may inherit conditions that make their enamel weaker or cause unusual enamel development, increasing their risk of tooth decay and staining. However, the biggest impacts often come from how we care for our teeth, including our oral hygiene habits and what we eat and drink.
Conclusion
In conclusion, at Review Health, we recognize that tooth decay brown stain on teeth is frequently caused by factors such as poor oral hygiene, smoking, and consuming dark-colored foods and drinks. Fortunately, many of these external spots on the teeth are removable and can be prevented with proper dental care. However, it’s important to note that sometimes brown spots are more than just cosmetic issues. They may signal underlying medical conditions or be side effects of medications. If you find that brown spots persist despite using over-the-counter treatments, or if they occur alongside other symptoms, we advise consulting a healthcare professional. Getting expert advice is crucial to addressing any serious health issues and maintaining optimal oral health.