Blurry Vision – Are you experiencing moments of uncertainty, where your surroundings appear hazy and focusing becomes a struggle? Do you find yourself squinting, wondering if it’s just fatigue or something more? If you’re experiencing these symptoms, you’re not alone.
In this blog, we explore the complexities of blurry vision, investigating its various triggers, potential remedies, and when to seek professional help. Whether you occasionally experience blurriness or seek insights into managing chronic vision issues, “Defining Beauty” at Review Health is your comprehensive guide to clarity. Join us as we navigate through the world of blurry vision, shedding light on ways to achieve and maintain clear sight.
Summary of Blurry Vision
Blurry vision is a common concern that can affect one or both eyes, resulting in a lack of sharpness and clarity in your vision. It can manifest as a partial or complete impairment of your visual field. Many individuals report blurry vision as the primary symptom when seeking medical attention for vision-related issues.

What Causes Blurry Vision?
Various factors can contribute to blurry vision. Here are some common causes:
- Refractive Errors: Astigmatism, farsightedness, and nearsightedness can lead to difficulties in focusing images correctly. Corrective measures such as eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery can often address these issues.
- Dry Eye Syndrome: This condition occurs when the eyes do not produce enough tears or when the tears evaporate too quickly. Symptoms may include a sensation of having a film over the eyes, along with itching, redness, and discomfort. Artificial tears are commonly used for treatment.
- Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): This progressive condition affects the central vision, making it challenging to see objects directly in front of you. AMD is particularly prevalent among older individuals.

- Diabetic Retinopathy: People with diabetes are at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy, which can lead to vision impairment and even blindness. This condition weakens the blood vessels in the retina.
- Glaucoma: Increased fluid pressure within the eye can damage the optic nerve, resulting in partial vision loss or blindness.
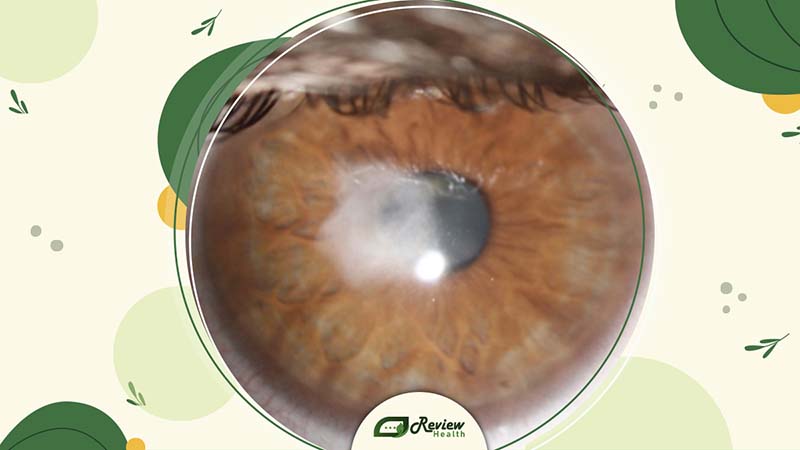
- Cataracts: Clouding of the eye’s lens can cause blurry vision, decreased contrast sensitivity, and halos around lights, especially in low-light conditions.
- Optic Neuritis: Inflammation of the optic nerve, often associated with conditions like multiple sclerosis, can cause blurry vision, particularly in one eye.
- Inherited Optic Nerve Disorders: Some genetic disorders can lead to optic nerve damage, though this is less common compared to other causes of blurry vision.
- Corneal Scars: Deficiencies in vitamin A, particularly prevalent in less developed regions, can result in scars on the cornea, leading to blurry vision.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment based on the underlying cause of blurry vision.
Common Symptoms of Blurry Vision
The symptoms of blurry vision can vary depending on factors such as age and the underlying cause. Here are some common symptoms associated with blurry vision:
Affected Vision Range: Blurriness may impact one eye, your entire field of vision, or specific areas within your sight. This could include peripheral vision, which encompasses what you see to the sides, above, and below your central vision.
Refractive Errors: Conditions like near-sightedness and far-sightedness can accompany blurry vision. For instance:
Near-sightedness may cause distant objects to appear blurry or out of focus.
Far-sightedness may result in close objects appearing blurry while distant objects remain clear.
Additional Symptoms: Blurry vision can be accompanied by other common symptoms such as:
- Double vision
- Seeing halos around bright objects
- Squinting
- Headaches
- Diminished color perception
- Fatigue

Recognizing these symptoms can help in identifying the underlying cause of blurry vision and seeking appropriate medical attention.
How to Treat Blurry Vision Naturally At Home
To address blurry vision naturally at home, consider the following treatments and lifestyle adjustments tailored to the underlying cause:
Rest and Recovery:
Ensure adequate sleep to support eye health.
Follow the 20-20-20 rule: Every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break to look at an object at least 20 feet away to alleviate eye strain.

Eye Lubrication:
For dry eyes, blink frequently or apply a warm compress to stimulate oil glands in the eyelids.
Use over-the-counter artificial tears to keep the eyes lubricated and prevent dryness.
Improve Air Quality:
Use a humidifier, especially in dry climates, to maintain optimal moisture levels and prevent dry eyes.
Avoid direct airflow to the face, particularly while sleeping.
Quit Smoking:
Smoking can exacerbate various eye conditions, including dry eyes, AMD, cataracts, and optic nerve damage.

Avoid Allergen:
Minimize exposure to allergens by cleaning regularly, closing windows during high pollen seasons, and using air conditioning with allergen filters.
Consider antihistamine eye drops for allergy relief, available over-the-counter or by prescription.
Protect Eyes:
Wear sunglasses that block UVA and UVB rays to shield your eyes from harmful sun exposure.
Protect against wind and cold weather conditions to prevent irritation.

Consume Food Rich in Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
Incorporate omega-3 rich foods into your diet, such as fatty fish, flax seeds, and walnuts, to potentially alleviate dry eye symptoms.
Consult a healthcare professional before taking omega-3 supplements, especially if you have an increased bleeding risk.
Consume a higher amount of Vitamin A:
Consume foods rich in vitamin A, such as dairy, liver, fish, sweet potatoes, carrots, kale, red peppers, spinach, and butternut squash, to support eye health and prevent dryness.
Clean Your Contact Lens:
- Follow proper hygiene practices when handling and cleaning contact lenses to prevent eye infections.
- Avoid wearing contact lenses while sleeping to reduce the risk of complications.
These natural approaches can complement professional medical advice and treatment for blurry vision, promoting overall eye health and clarity of vision.
Can Blurry Vision Be Prevented?
While it may not always be possible to completely prevent blurry vision, there are steps you can take to minimize the risk and promote overall eye health:
Follow Medical Advice: If you have underlying health conditions like diabetes, adhere to your healthcare provider’s recommendations to manage the condition effectively. Controlling conditions that can affect vision can help prevent or reduce the severity of blurry vision.
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy lifestyle by incorporating nutritious foods and regular physical activity into your routine. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports eye health and overall well-being.
Schedule Regular Eye Exams: Schedule regular eye examinations with an eye care professional. Routine check-ups can help detect potential vision problems early and allow for prompt treatment, reducing the risk of blurry vision and other eye-related issues.

By prioritizing your eye health and implementing these preventive measures, you can take proactive steps to minimize the occurrence of blurry vision and maintain optimal visual clarity.
Can Eye Diseases Cause Blurry Vision?
Yes, various eye diseases and conditions can lead to blurry vision. These include:
Refractive Errors: Conditions like near-sightedness, far-sightedness, presbyopia, and astigmatism can affect the eye’s ability to focus light, resulting in blurry vision.
Dry Eye Syndrome: Insufficient tear production or poor tear quality can cause discomfort and blurry vision.
Cataracts: Clouding of the eye’s lens can impair vision, causing objects to appear blurry or hazy.
Glaucoma: Increased intraocular pressure can damage the optic nerve, leading to vision loss and blurry vision.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): Degeneration of the macula, a part of the retina responsible for central vision, can result in blurry or distorted vision.
Eye Infections, Injuries, or Corneal Damage: Trauma or damage to the eye, including infections or corneal injuries, can cause temporary or permanent blurry vision.
Retinal Problems: Conditions like diabetic retinopathy, which affects the blood vessels in the retina, can lead to vision impairment and blurry vision.
It’s essential to seek prompt medical attention if you experience persistent blurry vision, as it could be a symptom of an underlying eye condition that requires treatment. Regular eye examinations are also crucial for early detection and management of eye diseases.
How to Cure Blurry Vision Naturally?
If you’re experiencing blurry vision due to factors like corneal abrasion, allergies, eye strain, weather conditions, or dry eyes, you can try natural remedies and lifestyle changes to promote eye health. Here are some non-medical tips:
Rest and Sleep:
Ensure you get adequate rest and sleep to allow your eyes to recover from extended periods of use, especially with electronic devices. Consider following the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break by focusing on an object at least 20 feet away.
Eye Yoga:
Practice eye yoga or relaxation exercises to relieve eye strain and strengthen eye muscles. These exercises involve various eye movements that can help alleviate blurry vision.
Healthy Diet:
Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids into your diet to support eye health and combat dry eyes. You can do this through omega-3 supplements or by consuming foods like fish, walnuts, and flax seeds.
Increase your intake of vitamin A-rich foods such as dairy products, kale, carrots, red peppers, spinach, and sweet potatoes. Vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy vision and may help alleviate dry eyes.
By incorporating these natural approaches into your daily routine, you can support your eye health and potentially alleviate symptoms of blurry vision caused by certain conditions or lifestyle factors. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional if you experience persistent or severe vision problems.
Frequently Asked Questions?
Can Dry Eyes Cause Blurry Vision?
Yes, dry eyes can indeed cause blurry vision. When there are issues with the quality or production of tears, which are essential for keeping the eyes lubricated and maintaining good vision, it can lead to dry eyes. When the eyes dry out due to tear production problems, it becomes challenging to focus, resulting in blurry vision.
Is It Possible to Have Sudden Blurry Vision in One Eye?
Experiencing sudden blurry vision in one eye is not uncommon and may not always indicate a serious medical emergency. However, it can be a warning sign of underlying conditions that may require medical attention, especially if the blurriness persists.
Is It Possible to Have Sudden Blurry Vision in Both Eyes?
Yes, sudden blurry vision in both eyes can occur due to various reasons, ranging from minor issues to more serious medical emergencies. Causes may include refractive errors like nearsightedness or farsightedness, eye strain, presbyopia, among others. Corrective measures such as eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery can address many of these issues.
Can Blurry Vision Be Related to a Headache?
Blurry vision can indeed be associated with headaches, particularly migraine headaches. Approximately one-third of people who experience migraines also report visual disturbances such as blurry vision. Migraine headaches often involve severe throbbing or pulsing pain in the head, sometimes accompanied by visual disturbances.
Does Cataracts Cause Blurry Vision?
Yes, because of this cloudiness, the light can’t pass through the lens properly. So, instead of a clear picture, you get a blurry one. As the cataract gets worse, it becomes harder to see clearly because more and more of the lens is covered by the cloudy part. That’s why people with cataracts often have blurry vision that keeps getting worse.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blurry vision can arise from various factors, including poor vision, which is quite common. Fortunately, there are ways to address this issue effectively, such as wearing glasses or contact lenses. However, other factors like migraines or underlying health conditions such as glaucoma or eye infections can also contribute to blurry vision.
It’s important to understand that blurry vision can manifest differently, ranging from occasional blurriness to more persistent or even permanent impairment. Additionally, accompanying symptoms like cloudy vision, headaches, or dizziness could indicate underlying health issues that require prompt medical attention.
Any sudden or significant changes in vision warrant a visit to a healthcare professional to identify the root cause and appropriate treatment. By remaining vigilant and seeking timely medical care when necessary, individuals can protect their vision and overall well-being.
If you’re interested in learning more about eye health and beauty, consider exploring our blog “Defining Beauty” at Review Health for further insights and tips on maintaining healthy vision.
Source:
- What Causes Blurred Vision?
- Eye conditions that can cause blurred vision

